CRISPR gene editing has emerged as a groundbreaking tool in modern biotechnology, revolutionizing the way we approach genetic diseases and modifications. This powerful technology enables scientists to precisely alter DNA sequences, opening new avenues for potential cures such as a sickle cell cure that could drastically improve the lives of those suffering from this debilitating condition. However, alongside the promise of these advancements arise critical discussions surrounding gene editing ethics and the implications for health justice in our society. As researchers explore the potential of CRISPR technology to not only treat but perhaps even eradicate hereditary diseases, the genetic modification risks cannot be overlooked. Balancing the benefits of such innovations with ethical considerations is essential as we navigate the uncharted waters of genetic manipulation.
The advent of CRISPR technology, often referred to as gene-editing, has sparked a revolution in the life sciences field, offering unprecedented capabilities to modify genetic material. Scientists are now able to make targeted changes to DNA, raising questions about the broader implications of such techniques, including the moral dilemmas associated with editing human genomes. This emerging scientific frontier has ignited debates about the responsibilities we hold when it comes to genetic alterations, particularly in the context of curative solutions for conditions like sickle cell disease. Furthermore, as society grapples with the challenges of health equity and the unintended consequences of genetic modification, the conversations around genetic editing ethics have never been more vital. Therefore, it is crucial to assess how these advancements will shape our understanding of human variation and societal implications.
The Promise of CRISPR Gene Editing
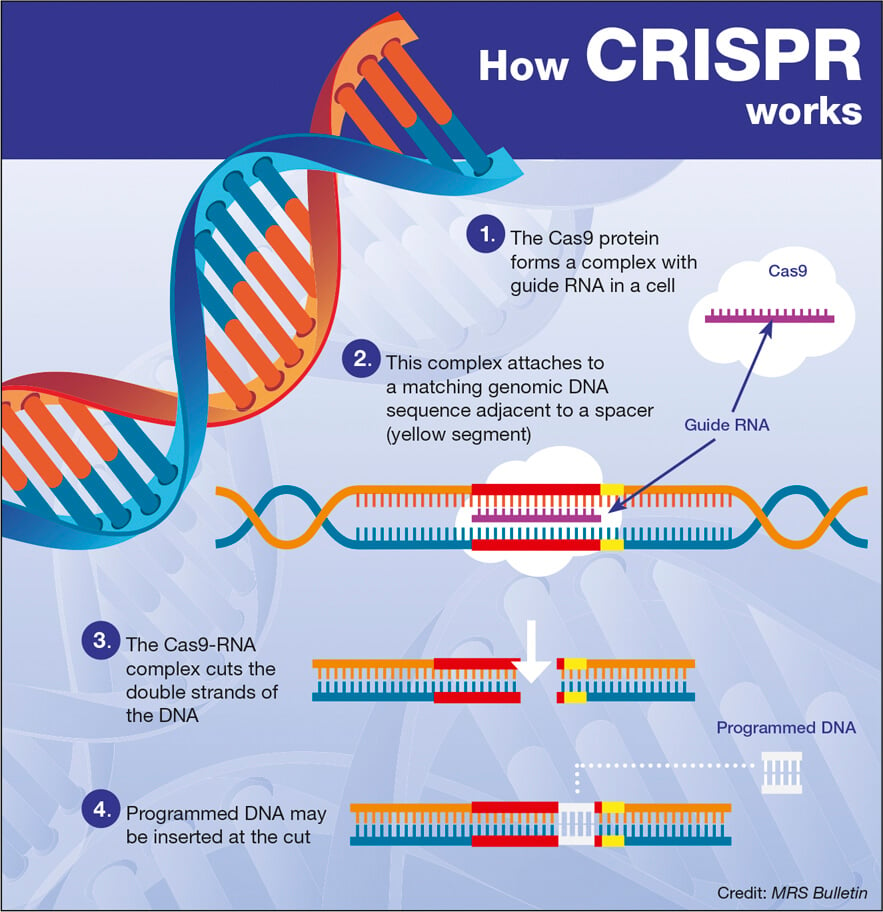
CRISPR gene editing represents a groundbreaking advancement in the world of genetic modification, providing the potential to rectify genetic disorders that have long plagued humanity. The technology allows for precise alterations at the DNA level, enabling scientists to target specific genes responsible for diseases like sickle cell anemia. This breakthrough not only offers hope for existing patients but also sparks debate on the ethical implications of altering human genetics. The promise of CRISPR lies in its ability to change the course of some lives, providing a pathway toward more effective treatments and potential cures.
However, while the scientific community is largely optimistic about CRISPR’s potential, the risks associated with genetic modifications cannot be overlooked. With unprecedented power comes the responsibility to tread carefully, as gene editing could lead to unforeseen complications. From unintended genetic consequences to the ethical conundrums surrounding ‘designer babies,’ the discussion surrounding CRISPR gene editing is as much about science as it is about philosophy and ethics. Ultimately, the potential of gene editing must be balanced with a thorough assessment of the ethical landscape it evokes.
Ethical Implications of Gene Editing Technology
As advancements in CRISPR gene editing continue to unfold, ethical questions surrounding the manipulation of human DNA become increasingly pressing. Experts like Neal Baer highlight that society must grapple with the implications of using gene editing for non-life-threatening conditions, such as gender or intellectual traits. The question arises: who determines which traits are worthy of alteration? These ethical dilemmas make it essential for society to engage in discussions about the moral responsibilities that accompany such powerful tools. Without clear ethical guidelines, the line between beneficial treatment and eugenics can easily blur.
Moreover, the disparities in access to gene editing technology pose significant ethical challenges. As noted during the Science Center talk, the exorbitant costs associated with CRISPR treatments (like the $2.2 million price tag for sickle cell cure) raise serious issues of health justice and equity. Those in lower socioeconomic statuses may find themselves unable to access potentially life-saving interventions, further widening the gap between the ‘haves’ and the ‘have-nots’ in healthcare. This inequity prompts a critical examination of who gets to benefit from innovations in genetic technology and reminds us that ethical considerations must extend beyond the realm of science into the canvas of social justice.
Sickle Cell Cure and Public Health Considerations
The potential to cure sickle cell disease using CRISPR technology is a beacon of hope for many individuals suffering from this painful condition. By targeting and editing the genes responsible for the disease, scientists have demonstrated the ability to alleviate symptoms and dramatically improve the quality of life for patients. This breakthrough not only shines a light on the capabilities of modern medicine but also signifies a new era where genetic disorders can be addressed at their source, rather than merely managing symptoms. However, the high cost associated with this treatment invites scrutiny regarding its availability and affordability among diverse populations.
Public health implications of the sickle cell cure go beyond individual patient care. As discussions unfold around who will access CRISPR treatments, it’s vital to consider the broader impact on healthcare systems and society at large. For instance, if cures become restricted to affluent patients, what does this mean for public health initiatives aimed at eradicating sickle cell disease globally? Stakeholders must engage in dialogue about equitable distribution and health policies that ensure all communities, regardless of socioeconomic status, benefit from these scientific advancements. Balancing innovation with public health priorities is essential for fostering a just health landscape.
Health Justice and Genetic Innovations
The rapid progress in gene editing technologies like CRISPR calls into question the concept of health justice, particularly in how these innovations are integrated into healthcare systems. As noted by Brendel during her talk, advancements in medical science often enhance the capabilities of those who can afford them while leaving underserved populations behind. Health justice involves ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their economic status, have access to emerging medical treatments. The disparities in access to technologies such as CRISPR raise concerns about the societal implications of genetic innovations, highlighting the importance of equitable healthcare practices.
Efforts towards health equity necessitate proactive measures to address the barriers faced by marginalized communities. This includes engaging in policy funding that prioritizes equitable access to gene editing technologies and ensuring that clinical trials are inclusive of diverse populations. By focusing on health justice, we can work to prevent a future where groundbreaking medical advancements only serve to widen the existing inequalities in healthcare. As CRISPR technology evolves, a commitment to inclusive and fair practices must accompany its application, ensuring that every individual has the opportunity to benefit from these advancements.
Navigating Genetic Modification Risks
Editing the human genome using CRISPR brings forth a mixture of excitement and apprehension, primarily due to the potential risks involved. While the technology offers the possibility of addressing genetic disorders, there are valid concerns about unintended effects, such as off-target edits that could lead to new or exacerbated health issues. This unpredictability underscores the need for extensive research and consultation within the scientific community to develop safe practices in gene editing. As we tread into this new territory, a cautious approach that prioritizes patient safety and thorough risk assessments becomes essential.
In addition to biological risks, the ethical and social ramifications of genetic modification demand careful consideration. The prospect of ‘designer babies’ and other forms of eugenics can give rise to societal tensions and moral dilemmas regarding what constitutes acceptable genetic alterations. Fostering a dialogue that includes diverse perspectives—from ethicists to patients—can help navigate the complex landscape of genetic modification. By addressing risks comprehensively and ethically, the global community can harness the benefits of CRISPR while safeguarding against potential abuses stemming from its implementation.
Public Discourse on CRISPR Technology
Public understanding of CRISPR technology is crucial as advancements continue to emerge in this dynamic field. Engaging the public in discussions about the benefits and risks associated with genetic editing can help foster informed opinions and participation in potential regulatory measures. Increased transparency in research and clinical applications of CRISPR can enable communities to voice their concerns and contribute to shaping the future of gene editing. This public discourse can serve as a foundation for establishing ethical frameworks that guide the responsible use of CRISPR technology.
Moreover, involving diverse stakeholders—including ethicists, scientists, healthcare providers, and the general public—creates a rich dialogue that considers multiple viewpoints and experiences. This collective engagement is essential for addressing the societal impact of gene editing technologies and for promoting pathways that uphold health justice and equity. As gene editing continues to evolve, fostering an informed public discourse will be essential in ensuring that technological advancements are aligned with societal values and ethical considerations.
Future of Genetic Editing: Opportunities and Challenges
The future of genetic editing is rife with both opportunities and challenges that stem from the use of CRISPR technology. As researchers explore new applications for gene editing, from curing genetic diseases to enhancing agricultural productivity, there is immense potential to reshape various aspects of health and society. However, these advancements also come with an inherent responsibility to manage the implications of such powerful tools. Ensuring that future innovations align with ethical standards and public expectations is crucial as society grapples with the possibilities of genetic modification.
Additionally, navigating the future of genetic editing requires addressing regulatory frameworks that can adapt to the rapid pace of scientific progress. Policymakers must assess current regulations and determine how they can promote innovation while safeguarding against potential abuses. Striking this balance will be vital in maximizing the benefits of CRISPR technology and ensuring that diverse populations can access these life-changing advancements. As we look ahead, collaborative efforts between scientists, ethicists, and legislators will be essential in guiding the responsible path forward for genetic editing.
Comparative Analysis of Gene Editing Technologies
While CRISPR gene editing offers a revolutionary approach to genetic alteration, it is important to consider it alongside other gene editing technologies, such as TALENs and ZFNs. Each method has its unique advantages and limitations, and a comparative analysis reveals valuable insights into their applications and ethical concerns. For instance, while CRISPR is celebrated for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, TALENs and ZFNs are known for their precision, albeit at a higher expense and complexity. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the appropriate tool for specific applications and minimizing risks.
Furthermore, comparing these technologies allows for an exploration of their respective ethical implications. As with CRISPR, TALENs and ZFNs raise similar concerns about unintended consequences and the potential for misuse. This comparative analysis emphasizes the importance of transparent discussions surrounding all gene editing methodologies, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding their use. Ultimately, fostering a collaborative environment among researchers and ethicists can lead to advancements that harness the positive aspects of these technologies while carefully considering the ethical landscapes they inhabit.
International Perspectives on Genetic Modifications
As CRISPR technology evolves globally, it is essential to consider the various regulatory frameworks and societal attitudes towards genetic modifications in different countries. For instance, while some nations may embrace gene editing innovations, others impose strict regulations or outright bans, reflecting divergent cultural and ethical views on the practice. Understanding these international perspectives provides valuable context for advancing gene editing technologies responsibly and ethically across borders. Engaging in global dialogue can help harmonize ethical guidelines and foster collaboration to address common challenges.
Moreover, international cooperation in gene editing research can lead to the sharing of best practices and lessons learned from various approaches. This exchange can improve governance and oversight while ensuring that emerging technologies benefit all humankind, not just a privileged few. It is crucial for the global community to work together to address the multifaceted implications of genetic modifications, promoting health justice and equity regardless of geographic boundaries. By learning from one another, nations can collectively navigate the future of genetic editing with a focus on ethical responsibility and societal benefit.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ethical implications of CRISPR gene editing?
CRISPR gene editing raises significant ethical implications as it challenges our understanding of human variation and health justice. Questions arise about who gets to decide the traits of future generations, especially concerning conditions like Down syndrome. Moreover, healthcare equity comes into play, as innovations in CRISPR technology could widen the gap between affluent and disadvantaged populations.
Can CRISPR gene editing cure sickle cell disease?
Yes, CRISPR gene editing has shown promise in curing sickle cell disease by editing somatic cells to remove the genetic mutations responsible for the condition. This groundbreaking approach enables patients to potentially lead healthier lives, but it also raises ethical questions about access and the costs associated with such treatments.
What are the risks of genetic modification using CRISPR technology?
The risks of genetic modification through CRISPR technology include unintended consequences that may arise from altering genes, potentially affecting various biological systems. For instance, editing a gene related to LDL cholesterol could impact insulin regulation and other metabolic processes. Monitoring and oversight are critical to address these risks responsibly.
How does CRISPR technology relate to health justice?
CRISPR technology intersects with health justice by emphasizing equitable access to genetic treatments. While advances in gene editing could provide significant health benefits, the high costs associated with these therapies, like the $2.2 million for sickle cell treatment, raise concerns about who can afford them and the implications for those who cannot.
Should CRISPR be used for genetic enhancement beyond curing diseases?
The use of CRISPR for genetic enhancement beyond disease curing is a contentious issue. It prompts debates about parental rights in choosing genetic traits for their children and the ethical ramifications of modifying human attributes. Opinions vary widely, with some arguing for caution and regulation to prevent ‘designer babies’ and others advocating for the potential personal and societal benefits.
What role does oversight play in CRISPR gene editing research and application?
Oversight is crucial in CRISPR gene editing to ensure ethical standards are met and to prevent potential abuses, such as germline editing without regulatory checks. As gene editing advances rapidly, international collaboration and monitoring are necessary to address discrepancies in regulatory practices across countries, particularly in nations with less stringent oversight.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Ethical Considerations | The morality of using CRISPR to change human attributes raises fundamental questions about human identity. |
| Gene Editing Capabilities | CRISPR technology allows for editing both somatic and germline genes, potentially curing genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia. |
| Cost Implications | The cost of gene manipulation, such as the $2.2 million price tag for sickle cell treatment, raises fairness issues. |
| Social Justice | There are concerns about how innovations benefit the wealthy, while underprivileged groups may not have access. |
| Potential for Misuse | Concerns regarding the unethical application of gene editing in military and enhancement contexts. |
| Unintended Consequences | Editing genes can have unforeseen effects due to complex interactions within biological systems. |
Summary
CRISPR gene editing represents a revolutionary advancement in genetic technology, offering the potential to cure debilitating diseases and reshape human attributes. However, it brings forth a host of ethical dilemmas, including the risks of altering human identity, social equity in healthcare access, and the potential misuse of this powerful tool. As we navigate these complex issues, it is crucial to establish regulations and ethical guidelines that govern the use of CRISPR to ensure that its benefits can be realized without compromising our moral values.