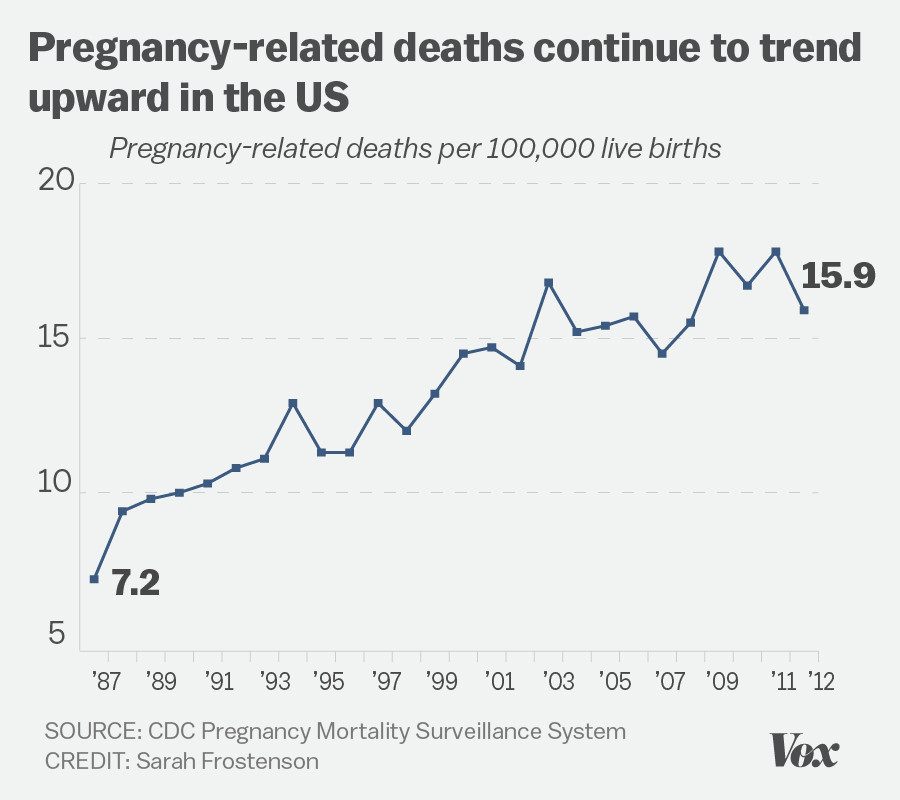
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have alarmingly continued to rise, highlighting a pressing public health crisis that demands immediate attention. The United States, which reports the highest maternal mortality rate among wealthy nations, experienced an increase in these tragic fatalities from 2018 to 2022, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. Over 80% of these deaths are preventable, yet systemic issues in pregnancy care and postpartum care have led to significant health disparities across different racial and ethnic groups. Furthermore, cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of these deaths, emphasizing the need for better health management during and after pregnancy. Tackling this alarming trend requires a comprehensive approach to enhance quality of care and eliminate disparities in maternal health outcomes.
The rising number of maternal fatalities in the United States underscores a critical issue in the realm of maternal health, as the country grapples with one of the highest maternal mortality rates among its affluent peers. Terms such as “pregnancy-related fatalities” or “maternal deaths” reveal the severity of the situation, where systemic inequities and lack of effective maternity services exacerbate risks for women, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds. Chronic health conditions, notably cardiovascular complications, have increasingly contributed to these preventable tragedies, drawing attention to the need for improved pregnancy care and extended postpartum monitoring. As awareness grows, it becomes crucial to address the multifaceted factors that hinder progress in reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Thus, enhancing healthcare infrastructure and policy reform is vital to ensure that all women receive equitable and comprehensive healthcare before, during, and after their pregnancies.
The Increase in U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Recent studies indicate that pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are on the rise, highlighting a troubling trend within maternal health. Despite advancements in healthcare, America now leads high-income countries in terms of maternal mortality rates, revealing significant gaps in pregnancy care. More than 80% of these deaths are deemed preventable, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive reform in our maternal health systems. Between 2018 and 2022, reported pregnancy-related deaths increased, with alarming disparities based on factors such as race, ethnicity, and geographic location, suggesting that not all women receive equitable care.
The National Institutes of Health’s findings emphasize that certain demographics experience an even greater burden, with American Indian and Alaska Native women having nearly four times the maternal mortality rate compared to their white counterparts. Such disparities highlight systemic issues within healthcare frameworks, pointing to necessary improvements in pregnancy and postpartum care across varying states. Continued monitoring and intervention are critical to understanding these trends and effectively addressing the contributing factors.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates
The maternal mortality rate serves as a crucial indicator of healthcare quality within a country, reflecting the effectiveness of pregnancy and postpartum care provided to women. In the U.S., the numbers reveal a stark reality; chronic health issues—particularly cardiovascular diseases—significantly contribute to these deaths. This shift from hemorrhage as the leading cause to cardiovascular complications marks a critical change in the landscape of maternal health, demanding sustained attention and targeted policy changes. It is essential for healthcare providers and policymakers to address chronic conditions affecting reproductive-aged individuals to reduce this preventable mortality rate.
Moreover, many women may not be receiving adequate care during the most vulnerable times of their reproductive lives. The incorporation of systematic care practices and improved health education for expectant mothers is vital to mitigate risks associated with pregnancy-related death. Continuous, comprehensive pregnancy care must be prioritized, particularly for women at risk of chronic illnesses that can complicate pregnancies, allowing for timely interventions that can ultimately reduce maternal mortality rates.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial disparities in maternal health outcomes are a pressing issue within the U.S., with studies revealing that American Indian, Alaska Native, and African American women face disproportionately high maternal mortality rates. These disparities reflect more than just access to healthcare; they expose deep-rooted systemic biases and inequities that prevent certain populations from receiving the quality care they deserve. For instance, factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and healthcare access play significant roles in the reproductive health challenges faced by these communities.
Efforts to close this gap require a multifaceted approach that includes increasing awareness about the disparities in maternal health among healthcare professionals, implementing community-centered health programs, and advocating for policies that support equitable healthcare access. Programs focused on maternal education, including proper prenatal and postpartum care, can empower women with the knowledge necessary to advocate for their health and wellbeing, and ultimately reduce pregnancy-related deaths.
The Role of COVID-19 in Maternal Mortality
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic coincided with a notable rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, highlighting the interconnectivity of public health crises. As healthcare systems became overwhelmed, maternal care often took a backseat, leading to missed prenatal appointments and reduced access to necessary resources. The disruption of routine care exacerbated existing vulnerabilities, particularly for women of color and those with pre-existing health conditions, revealing a significant challenge in maternal health care amid unprecedented times.
The long-term implications of the pandemic on maternal mortality rates necessitate rigorous examination and adjustment of healthcare delivery systems. Addressing health disparities that became more pronounced during this time is crucial as we move forward. There must be a proactive approach to ensure that pregnant individuals can access robust healthcare services, especially in emergency situations, which can include telehealth solutions and enhanced community outreach to safeguard the health of mothers and their infants.
Cardiovascular Disease as a Leading Cause of Maternal Death
Research indicates that cardiovascular diseases have emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., marking a significant concern for maternal health. This shift necessitates an urgent reevaluation of care strategies, especially given the rising rates of chronic conditions such as hypertension that contribute to these outcomes. Providers must improve monitoring and management of cardiovascular health among pregnant individuals, ensuring that all women receive adequate screenings and interventions that can mitigate risks associated with pregnancy.
Understanding how chronic health issues like hypertension affect maternal health is critical in crafting targeted prevention strategies. Enhanced prenatal care that addresses these conditions can reduce the likelihood of severe complications during pregnancy and postpartum recovery. Investing in health education and systemic support for women at risk of cardiovascular disease is essential in altering the current trajectory of maternal mortality rates, thus promoting healthier pregnancies.
The Importance of Extended Postpartum Care
Extended postpartum care is often overlooked within the conversation surrounding maternal health, yet it is a crucial component of effective healthcare. Recent studies reveal that late maternal deaths—occurring between 42 days and one year post-pregnancy—constitute a significant portion of total maternal mortality. This highlights the necessity of continuity in care beyond the traditional postpartum period of six weeks, as many health complications can arise after this time frame.
Designing healthcare systems that recognize the postpartum period as a continuum rather than a finite timeframe is vital. Developing policies that prioritize follow-up care and support for mothers during the critical months after birth can substantially reduce late maternal deaths and improve overall health outcomes. Emphasizing the need for comprehensive postpartum care resonates with the understanding that maternal recovery is a long-term process requiring sustained medical attention and support.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure
To combat the rising rates of maternal mortality and improve pregnancy-related outcomes, it is imperative to invest in public health infrastructure. As the current data indicates, the U.S. is not on track to improve its maternal health outcomes without significant changes in policy implementation and resource allocation. Strengthening community health programs, increasing research funding, and promoting effective health education initiatives can create environments conducive to better pregnancy care.
Moreover, advocacy for enhanced funding and resources must be at the forefront of efforts to combat health disparities. Building a robust infrastructure will not only equip healthcare systems to handle maternal health crises but also ensure that all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographical location, have access to high-quality care throughout their pregnancy and postpartum journeys.
Addressing Health Disparities in Maternal Care
Addressing health disparities in maternal care is essential for improving outcomes for all women. Disparities that exist across racial and ethnic lines reveal the urgent need for comprehensive strategies that target systemic inequities. This could include advocating for policy changes that promote equitable access to healthcare resources, as well as training healthcare providers to understand and address their own biases which may affect patient care.
By acknowledging and implementing strategies that address health disparities, we can create environments where all mothers receive the same high standard of care, regardless of their background. Empowering community organizations to play a proactive role in maternal care, alongside federal and state initiatives, can help ensure that health equity becomes a central tenet of maternal health policies.
Policy Recommendations for Improving Maternal Health
In light of the alarming trends regarding maternal mortality in the U.S., effective policy recommendations are essential to foster improvements in maternal health outcomes. These may include re-evaluating funding priorities to ensure that maternal health remains a focus within healthcare discussions, as well as expanding Medicaid coverage for postpartum care to provide women with comprehensive support after giving birth. Improving access to quality prenatal and postpartum care for marginalized populations will be crucial in bridging the current healthcare gaps.
Furthermore, establishing multi-disciplinary collaborations across healthcare sectors can yield more innovative solutions to maternal health challenges. Collaboration between obstetricians, public health officials, and community leaders can lead to localized programs that specifically address the unique needs of different populations while also prioritizing prevention and education as vital components of healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main factors contributing to the high maternal mortality rate in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. experiences a higher maternal mortality rate due to several factors including a fragmented healthcare system, unequal access to pregnancy care, and health disparities rooted in systemic bias and discrimination. Additional issues such as chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease also contribute to this alarming trend.
What measures can be taken to reduce pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
To reduce pregnancy-related deaths, it’s essential to enhance prenatal and postpartum care by implementing better healthcare policies and addressing systemic inequities. Innovative solutions and increased investment in public health infrastructure are necessary to improve the quality of care throughout the full pregnancy and postpartum periods.
How do health disparities affect maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Health disparities significantly influence maternal mortality rates, with groups such as American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing disproportionately higher rates. These inequalities arise from a combination of socio-economic factors, access to quality care, and systemic biases that persist across healthcare systems.
Why is postpartum care crucial in addressing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is vital as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur after delivery, often during the first year postpartum. Adequate care during this period is necessary to monitor and treat ongoing health issues, ensuring a continuum of care that significantly impacts maternal health outcomes.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in pregnancy-related deaths?
Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of such deaths. The rise in chronic conditions like hypertension, affecting younger and middle-aged women more frequently, underscores the need for proactive management during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
How does the definition of maternal mortality differ in the U.S. compared to international standards?
Internationally, maternal mortality includes deaths during pregnancy and up to 42 days postpartum, but the U.S. is moving toward a broader definition that considers deaths occurring up to one year after pregnancy. This shift acknowledges the critical health challenges women may face long after childbirth.
What can be done at the state level to improve maternal mortality rates?
At the state level, addressing policy disparities and understanding the factors contributing to varied maternal mortality rates can help improve outcomes. States can learn from those performing better by adopting best practices in maternal care and fostering greater collaboration among healthcare providers.
What impact has the COVID-19 pandemic had on pregnancy-related death rates in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic has notably impacted pregnancy-related death rates, particularly causing a spike in 2021. Although rates slightly declined afterward, they remained higher than pre-pandemic levels, indicating the need to evaluate and adapt maternal healthcare strategies in light of ongoing challenges.
Why is it essential to track and report maternal mortality accurately?
Accurate tracking of maternal mortality is crucial for identifying trends, understanding contributing factors, and guiding policy improvements. The introduction of specific tracking measures, such as pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates, has enhanced data quality and informed better maternal health initiatives.
What are the long-term solutions proposed for addressing maternal health in the U.S.?
Long-term solutions include investing in comprehensive public health infrastructure, enhancing access to quality maternity care, and fostering community-based initiatives that address disparities. Continued research and advocacy are necessary to ensure that maternal health remains a priority within the broader healthcare agenda.
| Key Points |
|---|
| More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, which continues to rise. |
| Between 2018 and 2022, pregnancy-related deaths increased from 25.3 to 32.6 per 100,000 live births. |
| Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest mortality rates. |
| Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of cases. |
| ‘Late maternal deaths’ are significant and need to be included in mortality considerations for better healthcare design. |
| There is a strong need for improved public health infrastructure and policy to address the rising rates of maternal mortality. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths remain a critical concern as the nation continues to lead in maternal mortality rates among high-income countries. Despite substantial potential for prevention, the rates have risen from 25.3 deaths to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022, showcasing significant disparities based on race and geography. Addressing the underlying causes, including chronic health issues and inequitable healthcare access, is crucial to reversing this troubling trend.