The neurological basis of social connection is an intriguing area of study that reveals the intricate wiring of our brains that fosters human relationships. As health professionals increasingly recognize social interaction as essential for overall well-being, recent neuroscience research has illuminated how our brains are wired to pursue our connections with others. This quest for social behavior is crucial not only for emotional satisfaction but also for maintaining mental health. By understanding the neurological circuits that underpin these social interactions, we can gain insight into various psychological disorders that stem from social disconnection. Ultimately, fostering strong human connections nourishes our minds in the same way that food and water do for our bodies.
Delving into the intricacies of the brain’s influence on interpersonal relationships provides a remarkable insight into why socialization is vital to our existence. The architecture within our neural systems, responsible for encouraging social behavior, operates similarly to mechanisms that fulfill our basic physiological needs. This intersection of neuroscience and social behavior highlights the profound importance of maintaining connections with others for optimizing mental health. Moreover, understanding this framework might explain how our relationships shape our emotional landscape and could offer new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Such knowledge emboldens us to appreciate the essential role that social interaction plays in our day-to-day lives.
The Neurological Basis of Social Connection
Social connection is increasingly recognized as a crucial element for mental health, paralleling our basic physiological needs. Recent neuroscience research has revealed that specific neural circuits in the brain govern our desire to seek social interactions, highlighting the neurological basis of social connection. By understanding these underlying mechanisms, researchers believe we can address public health concerns around loneliness and social isolation, similar to how we address hunger or thirst.
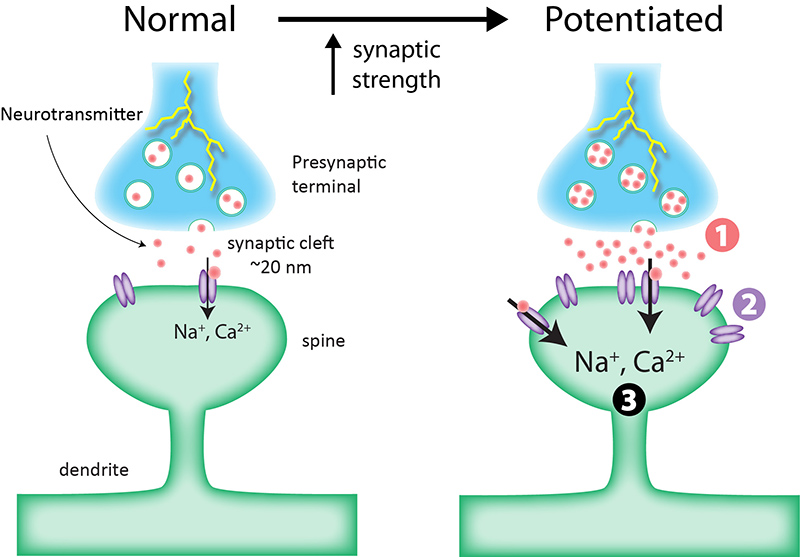
In their groundbreaking study, Ding Liu and his colleagues explored the hypothalamus to identify neurons that activate during periods of social deprivation. Their findings suggest that the desire for connection may be driven by an instinctual aversion to isolation rather than solely a pursuit of pleasurable interactions. This insight not only deepens our understanding of social behavior but also paves the way for innovative approaches to treating mental health issues where social engagement is impaired.
The Role of Social Interaction in Mental Health
Social interaction plays a vital role in mental well-being, as evident in various studies linking social behavior to psychological health. Engaging with others not only fosters emotional support but also enhances the regulation of stress and anxiety levels. Neuroscience research indicates that positive social interactions can facilitate the release of neurotransmitters such as oxytocin and serotonin, which reinforce feelings of happiness and contentment. However, when these interactions are lacking, individuals may experience heightened feelings of loneliness, subsequently affecting their mental health.
As a notable contributor to mental health, social interaction can improve cognitive functions and emotional resilience. Liu’s research indicates that the absence of social contact can become detrimental over time, leading individuals to develop aversive responses to social behavior. Rather than solely relying on external social stimulation, understanding the intrinsic need for social connectivity can inform strategies for fostering healthier relationships and promoting well-being.
Understanding Social Behavior through Neuroscience Research
Neuroscience research offers profound insights into the nature of social behavior, unveiling the biological frameworks that dictate our social needs. By examining the interactions of neurons within the hypothalamus, researchers like Liu have begun to elucidate how social desire might parallel other physiological needs. This research underscores the necessity of social bonds for overall mental health and provides a compelling reason to prioritize social interaction as part of health care practices.
Furthermore, investigating social behavior through a neurological lens can enhance our grasp of various mental health disorders characterized by impaired social function, such as autism and schizophrenia. As scientists delve deeper into the biological basis of social connections, they can develop targeted therapies that address the root causes of social dysfunction, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals struggling with these conditions.
The Impact of Isolation on Human Connections
Isolation can significantly alter the dynamics of human connections, leading to various psychological challenges. Research has shown that prolonged periods of social deprivation not only create a longing for social interaction but can also warp perceptions of social engagement negatively. As highlighted by Liu’s study, when mice were isolated for extended periods, they experienced a shift in their preference for social behavior, preferring isolation over interaction. This phenomenon has dire implications for humans, particularly in an age where meaningful offline social interactions are increasingly rare.
The implications of isolation and its impacts on human psychology are particularly stark given the rise of digital communication. While online interactions can offer a semblance of connection, they lack the physical touch that enhances social bonds. Liu suggests that human behavior hinges on tactile cues, emphasizing the importance of direct physical interactions in fostering healthy relationships. As social creatures, humans thrive on physical presence, and acknowledging these needs is paramount in an increasingly disconnected world.
The Biological Foundations of Human Connections
Understanding the biological underpinnings of human connections highlights the critical role these relationships play in our overall health. Liu’s research into the neural circuits associated with social needs reveals that our brains are wired for connection, mirroring the mechanisms involved in other basic needs like hunger and thirst. This suggests that social connectivity is not merely a luxury but a fundamental requirement for psychological and emotional stability.
Moreover, these biological insights can serve as a catalyst for developing interventions aimed at enhancing social engagement. By creating environments that encourage human connections, we can combat the adverse effects of social isolation, bolster mental health, and improve the quality of life. Ultimately, the future of mental health care could benefit significantly from strategies rooted in a nuanced understanding of our biological need for social interaction.
The Importance of Touch in Social Interaction
Touch serves as a foundational element in social interaction, deeply influencing the way we form and maintain our human connections. Liu’s findings indicate that sensory experiences, particularly tactile interactions, are crucial for fulfilling social needs. The preference shown by mice for a soft cloth tunnel over a bare plastic one after periods of isolation underscores how vital touch is for establishing comfort and security within social relationships.
For humans, the importance of touch cannot be overstated. From hugs to handshakes, tactile interactions convey emotions and reinforce bonds between individuals. In a world increasingly dominated by virtual communication, recognizing and prioritizing the significance of physical touch could help mitigate feelings of isolation and loneliness, ultimately promoting stronger social ties and better mental health.
Exploring the Psychological Impact of Social Needs
Social needs extend beyond mere companionship; they are linked to various psychological outcomes central to our overall well-being. Liu’s research suggests that recognizing the biological aspects of our social behaviors could lead to improved understanding and treatment of mental health disorders. The interplay between social connection and psychological states indicates that fostering human relationships can serve as a powerful buffer against mental health challenges.
Additionally, as societal structures evolve, the psychological impact of reduced physical interactions is increasingly recognized. Addressing the roots of social reluctance can lead to innovative therapeutic approaches that encourage engagement and connection, benefiting both individual and communal mental health. By acknowledging social needs as fundamental, we can promote healthier social landscapes that nurture our psychological well-being.
Strategies for Enhancing Social Engagement
Given the neuroscience findings surrounding social connection, developing strategies to enhance social engagement becomes imperative. Health professionals can leverage this understanding to design interventions that encourage meaningful interactions, be it through community programs or therapeutic settings. These initiatives can focus on creating environments where individuals feel safe and motivated to connect, drawing on the instinctive need for social interactions.
Moreover, integrating technology to foster social connectivity may provide significant benefits. Virtual platforms can be utilized to facilitate interactions that mimic physical presence, while also ensuring that they encourage active and engaging forms of communication. Over time, prioritizing such strategies can create a stronger societal foundation of support, wellness, and interpersonal connectivity, thus challenging the rising tide of social isolation.
Addressing Loneliness through Community Initiatives
To effectively tackle loneliness, community initiatives designed to foster social connections can be immensely beneficial. Programs that encourage volunteerism, social club participation, or group activities can create networks of support across different demographics. Such endeavors not only aim to reduce isolation but also promote a sense of belonging, ultimately influencing mental health positively.
The effectiveness of these initiatives lies in their capacity to create environments where individuals can share experiences and form friendships. By focusing on building strong community bonds, we can mitigate the negative impacts of loneliness on mental health and foster an atmosphere conducive to positive social behavior. Encouraging individuals to engage and connect can lead to enhanced overall well-being as the fundamental need for social interaction is met.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social connection according to recent research?
Recent research highlights that the neurological basis of social connection is interconnected with vital brain functions similar to basic needs like hunger and thirst. Studies, including those from the Catherine Dulac Lab, have focused on the hypothalamus, revealing how neurons regulate our desire for social interaction and the consequences of social deprivation.
How does social interaction impact mental health in terms of neuroscience research?
Neuroscience research indicates that social interaction is critical for mental health, with deficiencies contributing to conditions like depression and autism. Understanding the brain’s role in social behavior helps unravel the mechanisms behind these mental health struggles, emphasizing the importance of social connections for overall well-being.
What role does the hypothalamus play in social behavior and human connections?
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in governing social behavior by maintaining social homeostasis. Research shows that neurons in this area become active during social deprivation, driving the urge to connect with others, thus reflecting its importance in healthy human connections.
Can social isolation lead to changes in social behavior according to neuroscience studies?
Yes, neuroscience studies indicate that prolonged social isolation can lead to aversive responses toward social interactions. For example, research found that mice isolated for extended periods began to exhibit a dislike for social behavior, underscoring how detrimental long-term isolation can be to social behavior.
How does touch factor into the neurological basis of social connection?
Touch is vital for fulfilling social needs, as shown by research that demonstrates mice prefer tactile environments after periods of isolation. This finding indicates that touch is an essential component of social interaction and may have significant implications for understanding human social behavior.
What implications does the neurological foundation of social connection have for understanding relationships?
Understanding the neurological foundation of social connection provides insights into how social bonds influence relationships and mental health. Studies reveal that similar neural circuits manage social needs and physiological requirements, illustrating the foundational role of social connections in leading healthy, fulfilling lives.
How can knowledge of the neurological basis for social connection help address public health concerns?
Knowledge of the neurological basis for social connection can inform public health strategies by highlighting the importance of social interactions in preventing issues like social isolation. This understanding can lead to targeted interventions that improve mental well-being and foster community connections.
Why is social interaction considered a basic human need by health professionals?
Health professionals view social interaction as a basic human need akin to food and water because it significantly influences mental health and overall quality of life. As highlighted by the U.S. Surgeon General, social isolation poses a major public health crisis, reinforcing the necessity for social ties in human health.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection Importance | Viewed as a basic human need, akin to food and shelter. |
| Surgeon General’s Emphasis | Highlighted social isolation as a significant public health concern in 2023. |
| Research Study | Study published in Nature explores the neurological basis for social needs. |
| Research Insights | The study uncovers mechanisms encoding social needs in the hypothalamus. |
| Impacts on Mental Health | Engaging in social interactions mitigates issues related to mental conditions like autism, depression, and schizophrenia. |
| Study Hypothesis | Social interactions may be driven by the need to avoid negative feelings rather than seeking positive ones. |
| Isolation Effects | Extended isolation can make social interaction undesirable. |
| Role of Touch | Touch is an important aspect of social needs, similar to that observed in mice during experimentation. |
| Relevance to Humans | Understanding social needs could shed light on human interactions and potential impacts of a digital age. |
Summary
The neurological basis of social connection is fundamentally entwined with our biological and psychological needs. Recent research has highlighted that social interaction is just as crucial for human health as food and water, making it essential for understanding mental health and social behaviors. By investigating the brain’s mechanisms behind social needs, researchers have uncovered how social interaction can alleviate feelings of loneliness and isolation, revealing parallels to our basic physiological urges like hunger and thirst. This exploration is not only pivotal for those grappling with mental health issues but also emphasizes the inherent human need for socializing, particularly in an era where digital communication often substitutes face-to-face interaction.